Tax Returns
Tax returns are documents filed by individuals or businesses with the government to report their income, expenses, and other financial information for a specific period, usually on an annual basis. They are used to calculate the amount of tax owed to the government or any tax refunds owed to the taxpayer.
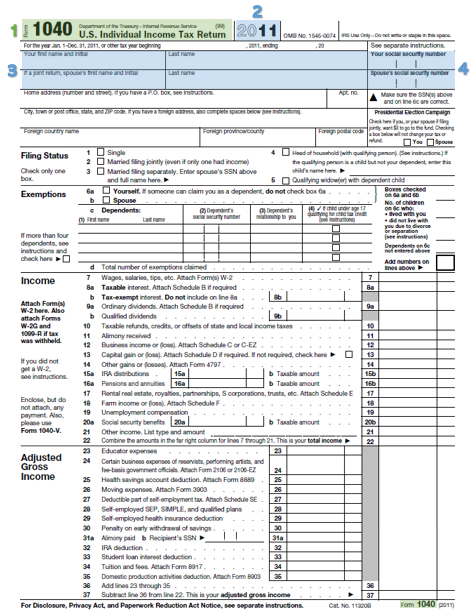
Context: Identifying the document.
Document title and tax form
Key takeaways: Important information.
Year
Filer’s (and spouse’s) name
Social security number
Tax Forms: Common tax schedules.
Form 1040 is the primary tax form used in the United States and is used to report their annual income, deductions, and tax liability.
Form 1120 is used by C corporations, which are corporations that are taxed separately from their shareholders. C corporations are subject to double taxation, meaning that the corporation pays taxes on its income, and then the shareholders pay taxes on any dividends they receive from the corporation.
Form 1120-S is used by S corporations, which are corporations that are taxed as pass-through entities. This means that the income and losses of the S corporation pass through to the shareholders' individual tax returns. S corporations are not subject to double taxation.
Schedule 1 is used to report additional income, adjustments to income, and certain tax credits.
Schedule A is used to report various deductible expenses.
Schedule B is used to report interest and dividend income earned from various sources.
Schedule C is used by self-employed individuals to report their business income and expenses.
Schedule D is used to report capital gains and losses from the sale or disposition of investments.
Schedule E is used to report rental income and expenses from real estate properties or income from partnerships, S corporations, estates, and trusts.